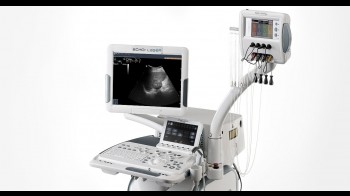
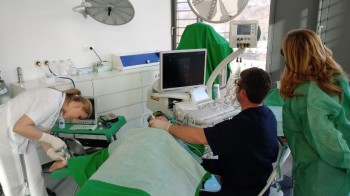
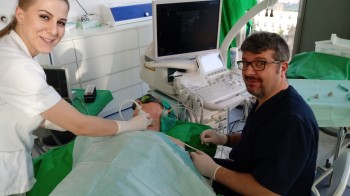
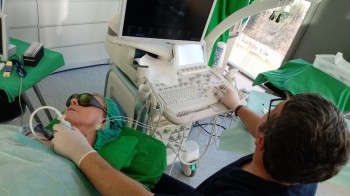
EchoLaser offers the chance to carry out ultrasound-guided micro-invasive treatments.
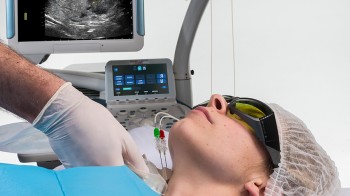
This is the first and only laser system integrated with a navigation, planning and simulation system. EchoLaser consists of an ultrasound and a multi-source laser (up to 4 sources): thanks to the ultrasound it is possible to diagnose lesions as well as monitor, in real-time, the correct positioning of laser light applicators and the actual extent of the damage caused to the lesion. TheEchoLaser Therapyis performed thanks to the laser and the optical fibers which transmit the laser energy into the tissues.
The laser components are manufactured by El.En. S.p.A., a world leader in the production of laser systems, and the ultrasound components are manufactured by Esaote S.p.A., a leading company in the production of ultrasound devices. EchoLaser is a complete surgical system as it comes with a disposable Kit of optical fibres designed with specific Guiding Systems and dedicated US software for the various tissues, according to the region where they are located.
Elesta chose a prominent Italian design firm (Rezzonico Design) to develop EchoLaser. EchoLaser can nicely sit on almost all Esaote ultrasound models, or on a customized trolley, if used with other ultrasound brands through ESI (EchoLaser Smart Interface).
EchoLaser allows the following:
Multi-fiber Approach
If required by the size or shape of the lesion to be treated, there is also the option of a multi-fibre approach. The laser energy is conveyed by the fibres simultaneously and, thanks to a synergic coalescence action, large volumes of coagulative necrosis can be obtained with perfect control of the borders, even in the case of large lesions.
- Option of treating lesions with a very wide size range (<1 cm with one fibre and over 5cm with four fibres);
- Option of adapting the treatment to the shape and position of the lesion;
- Option of treating lesions in high risk position (due to close vicinity to vital structures);
- Positioning of the needles with less trauma for the organ, also with the option of multiple repositioning.
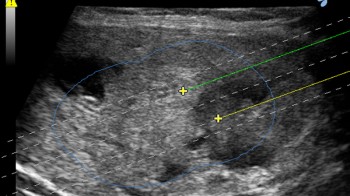
Ultrasound monitoring of the treatment
Ultrasound guidance allows the user to position several needles inreal-time quickly and safely, thereby reducing the operating times (with less stress for the patient, more economical treatments and more patients treated).
Micro-invasive technique with fine needles
The technique with very fine needles (<0.8mm) is completely non-traumatic and very well tolerated by the patient, ensuring fewer complications and side effects, a lower risk of infection and bleeding, fast recovery times and excellent aesthetic results without requiring anaesthesia.
Thanks to these features EchoLaser Therapy can be introduced in the sector of the micro-invasive techniques.
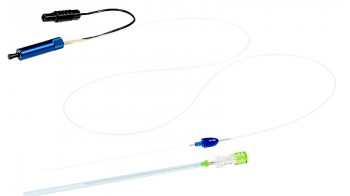
Disposable Optical Fibre Kit
The disposable optical fibre Kit contains a Chiba introducer needle (21G) with high echogenicity and a flat-tip optical fibre. The disposable optical fibre Kit, which is specific for each type of tissue depending on its location, has a colour code to help the operator to recognize it during the procedure. This is a patented kit.
Guiding Systems and dedicated Biopsy Software
The Guiding Systems on the Esaote probes have been designed for each kind of application to help the operator when positioning several fibres inside the lesion to be treated. The dedicated Biopsy Software for EchoLaser Therapy inside the US unit displays the guidelines on the screen for each different guide in order to allow for an evaluation of the best positioning of the applicator in reference to the size, morphology and position of the lesion.
Planning Software for neck application (ModìLite)
The Planning Software allows the operator to choose the safest needles insertion paths and the most suitable among various treatment options (number of fibers, pull-back number and applicators distance) for each specific case.
Radiofrequency ablation of thyroid nodules
Thermoablation techniques are no longer reserved only for benign nodes, but in well-chosen cases, they are also used to destroy malignant changes in the thyroid gland and surrounding lymph nodes.
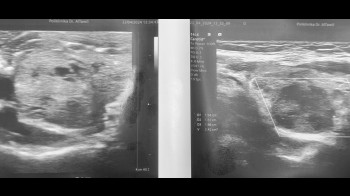
The focus has shifted to the earliest possible detection of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma, which is the most common (75-85% of all malignant changes are papillary carcinoma), while it is smaller than 10 mm, which is proven by puncture-FNAC of the node, when in selected cases it is enough perform laser or other thermal ablation of the node, and surgery is not necessary.
Studies on a large number of patients have shown that for such small tumors, thermoablation techniques are the same or more efficient than surgical methods, with incomparably lower intervention risks.
For the first time in 1931 Martin Kirschner, a German surgeon used RFA for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, in 1998 Solbiati published the first case of thyroid ablation, in 2012. The South Korean Radiology Society for Thyroid presents a protocol for the use of RFA, and since then massive use has begun.
Microwave ablation of thyroid nodules
It was first used for the treatment of thyroid nodules by Dr. Feng Bing, a Chinese radiologist, in 2012, and it quickly proved to be a powerful weapon in the treatment of thyroid nodules, even very large ones, or the treatment of multiple thyroid nodules/multinodular goiter.
Nodular thyroid disease is detected in up to 75% of the general population, particularly in the context of multinodular goiter. Even if most thyroid nodules are benign, treatment may be necessary, especially for subjective symptoms, cosmetic problems, patient's fear of malignant transformation.
If therapy is necessary, total/partial thyroidectomy is actually the standard of care, while iodine therapy has been used with poor results. Many studies suggest total thyroidectomy in the case of multinodular goiter, due to the risk of nodular recurrence in the rest of the thyroid, with the need for reintervention, which carries a higher risk of complications.
Surgery actually has some limitations, such as a 2-10% complication rate, iatrogenic hypothyroidism, hospitalization, general anesthesia, and scarring.
In recent years, non-surgical minimally invasive techniques (MITT) have been developed for the treatment of this pathology, primarily laser (LA) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA). Recently, microwave ablation (MWA) has been proposed for the treatment of thyroid nodules, taking into account its application in other organs, especially the liver, kidneys and lungs.
MWA has the following advantages over RFA: shorter treatment time, larger ablation zone, less heat spread effect.
All these methods are provided in our polyclinic, and with this we have made a significant step forward compared to other health institutions in the wider region in minimally invasive thyroid treatments (MITT)!
If You need more information, you want to consult whether you are a candidate for such treatment, you want to send your findings, you can do all this by email: tawildj@gmail.com or tawilstitnjaca@gmail.com
Watch Video: Thyroid Nodule ablation 1, 2, 3, 4. Mikrowave thyroid node ablation MWA 2, MWA 3, MWA 4, MWA 5